What is Fiber Optics? Definition, Types and Its Functions
Communication technology is developing rapidly, and one of the innovations that is the backbone of modern communication is fiber optics . Fiber optics is a transmission medium that uses glass or plastic fibers to transmit data in the form of light. This article will discuss the definition of fiber optics , its structure, how it works, and its advantages.
Understanding Fiber Optics
Fiber optics is a technology used to transmit data, voice, or images through glass or plastic fiber cables using light signals. This technology offers very high transmission speeds and more stable signal quality than traditional media such as copper cables.
Fiber optic cables are usually used for high-speed internet, telecommunications, and computer network systems that require large amounts of data transfer.
Optical Fiber Structure
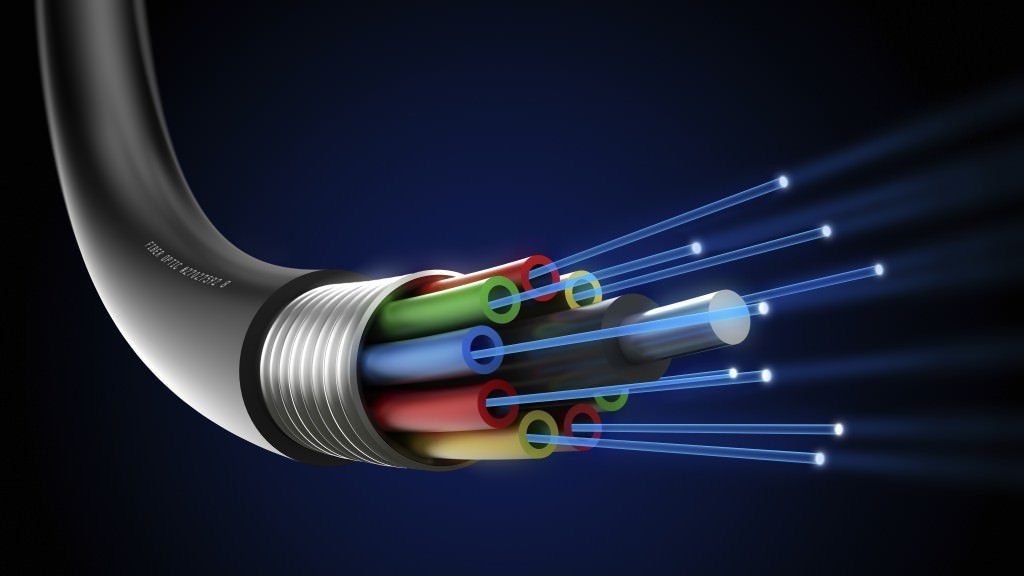
One of the reasons fiber optic cables are so efficient is their unique structural design. Here are the main parts of a fiber optic:
1. Inti (Core)
The core is the center of the fiber optic cable made of high-quality glass or plastic. This is where light is emitted to carry data. The diameter of the core can vary depending on the type of fiber optic used.
2. Cladding
Cladding is a layer that surrounds the core. The main function of the cladding is to reflect light back to the core so that the light remains inside the fiber even though it passes through bends. This is possible due to the difference in refractive index between the core and cladding.
3. Buffer/Coating
Buffer or coating is a protective layer that covers the cladding. Its purpose is to protect the fibers from physical damage, moisture, and other environmental factors.
4. Strength Member and Outer Jacket
Strength member is a component that provides mechanical strength to the cable, while the outer jacket is the outermost layer that protects the entire cable from environmental conditions such as heat, cold, or physical pressure.
How Fiber Optics Work
Fiber optics work based on the principle of total internal reflection. Here are the steps of how fiber optics work:
- Light Source
Data is encoded into light signals using lasers or LEDs. - Transmission Through the Core
The light carrying data is transmitted through the core, with the cladding reflecting the light to keep it inside the fiber. - Data Decoding
When it reaches the end of the cable, the light signal is translated back into data that can be read by the receiving device.
This process allows for fast, stable, and less disruptive data transfer compared to traditional copper cables.
Benefits of Fiber Optics
Fiber optic technology offers several advantages over other data transmission technologies:
- High Speed
Fiber optic cables are capable of transferring data at much higher speeds than copper cables. - Greater Bandwidth
Optical fiber can carry more data at the same time, making it ideal for high-bandwidth applications such as video streaming and real-time data communications. - Minimal Interference
Because data is transmitted in the form of light, fiber optics are not affected by electromagnetic interference which is often a problem with copper cables. - Long Transmission Distance
Optical fiber is capable of transmitting data over very long distances without experiencing significant signal degradation. - Data Security
Light signals are difficult to intercept, thereby increasing the security of the data being transmitted. - Lighter Size and Weight
Fiber optic cables are thinner and lighter than copper cables, making installation easier and reducing space requirements.
Conclusion
Fiber optics is a revolutionary technology that is the backbone of modern communications. With the ability to transmit data in the form of light through glass or plastic fiber cables, fiber optics offers superior speed, efficiency, and security compared to other technologies.
The unique structure of fiber optic cable , consisting of core, cladding, buffer, and outer jacket, enables fast and stable data transmission. With advantages such as high speed, minimal interference, and better security, fiber optic has become the main solution for communication needs in the digital era.
Understanding the concept of fiber optics and how it works and its benefits can help us maximize this technology in various fields, from the internet, telecommunications, to computer network systems.
Reference: linknet.id .
Author: Yazid Yusuf – Directorate of Information Technology Center